Understanding Electrical Panels: What They Are and How They Work
Definition and Purpose of Electrical Panels
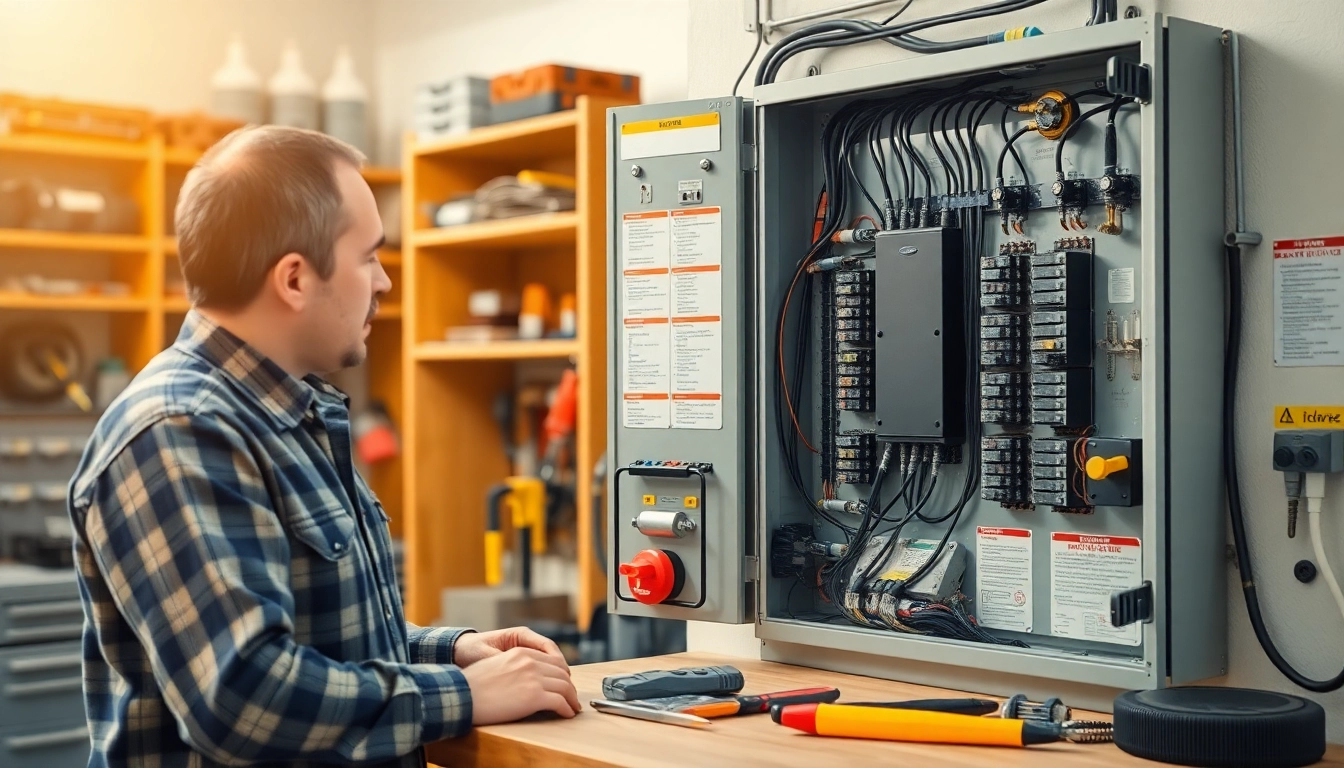
An electrical panel, often referred to as a breaker box or circuit breaker panel, serves a vital function in any residential or commercial electrical system. Acting as the hub through which electricity flows, it centrally manages electrical distribution throughout a property. The electrical panel connects to the main supply line and distributes power to various circuits, ensuring that each part of the electrical system can function efficiently while maintaining safety standards.
Components of an Electrical Panel
Electric panels are composed of several key components, each designed to protect and regulate the electrical supply:
- Main Breaker: This is a large switch that controls the flow of electricity from the main supply into the panel.
- Circuit Breakers: These smaller switches control individual circuits of electrical flow throughout the home, automatically shutting off in case of overload.
- Bus Bars: These metallic strips act as conductors, allowing electricity to flow from the main power source to the various breakers.
- Neutral and Ground Bars: These ensure that excess electricity is safely redirected to the ground, preventing shocks or fires.
How Electrical Panels Distribute Electricity
The electrical panel receives power from the main electricity line and routes it to different areas of the property via distinct circuits. Electricity flows into the panel, where the main breaker can cut the supply if necessary (for safety concerns). It then traverses through the bus bars to the designated circuit breakers, which control different sections of the electrical system — for instance, an individual circuit may power the kitchen, while another might serve the living room. Each circuit breaker monitors the amount of electrical current flowing through its circuit and intervenes when it detects a potential overload, shutting off the power to avoid damage or hazards.
Signs That It’s Time to Upgrade Your Electrical Panel
Identifying Electrical Panel Age and Wear
Electrical panels have a certain lifespan, typically between 20 to 30 years. Factors such as usage, environmental conditions, and overall maintenance can influence this. Older panels, particularly those made with outdated materials, may not handle modern electrical demands adequately. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for any physical signs of wear, such as rust, corrosion, or burning around the connections.
Common Symptoms of Panel Issues
Homeowners should be aware of several symptoms that may indicate that their electrical panel needs an upgrade:
- Frequent Circuit Breaker Tripping: If circuit breakers are tripping frequently without any added load on the circuits, it may mean your electrical panel is overloaded.
- flickering or Dimming Lights: Sudden flickering or dimming lights when using appliances can indicate insufficient voltage supply, hinting at problems within the panel.
- Burning Smells or Hot Patches: Any smell of burning or the presence of hot spots on the panel itself are serious signs that immediate diagnosis and maintenance are required.
Benefits of Updating Your Electrical Panel
Upgrading an electrical panel comes with a variety of benefits:
- Increased Capacity: A modern electrical panel can handle a larger capacity, accommodating newer appliances and technology.
- Enhanced Safety: Newer models come equipped with advanced safety features that help to prevent fires and electrical shocks.
- Improved Efficiency: A more efficient electrical panel can lead to lower energy costs, as it ensures that electrical systems are operating optimally.
Key Features to Look for in an Electrical Panel
Size and Amperage Considerations
When selecting an electrical panel, it is essential to consider the electrical load requirements for your home. Typical residential panels range from 100 to 200 amps; however, homes with high-power appliances or extensive electrical systems may require higher capacities. An electrician can assess your needs to determine the appropriate panel size.
Safety Features and Compliance
Safety should be a top priority when upgrading an electrical panel. Look for panels with features, such as:
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) breakers, which protect against electrical shocks.
- Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) breakers, which help to prevent electrical fires.
- Compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC) which ensures adherence to current safety standards.
Brand and Quality Recommendations
Choosing reputable brands is crucial for reliability. Consider established manufacturers, such as Square D, Siemens, or Eaton, which are known for their quality products and have good warranties. Researching customer reviews and ratings can also provide insight into their performance and reliability.
The Process of Upgrading Your Electrical Panel
Assessing Your Electrical Needs
The first step in the upgrade process involves a thorough assessment of your electrical needs. This includes evaluating the current and future electrical load, considering appliances, lighting, and technology you plan to use. It’s essential to work closely with a qualified electrician to ensure that all considerations are made.
Hiring a Qualified Electrician
Unless you have electrical training, upgrading a panel is a job for professionals. Hiring a licensed electrician is crucial as they understand local electrical codes and can ensure that all work meets safety regulations. They will provide necessary permits and handle inspections, which are critical steps in the upgrade process.
Steps Involved in the Upgrade
The upgrade process typically follows these steps:
- Power Shutdown: The electricity supply should be switched off to prevent any accidents during the installation.
- Removal of the Old Panel: The existing electrical panel is carefully removed, and wiring is assessed for safety and compatibility.
- Installation of New Panel: The new panel is mounted, and wiring is connected according to the specifications required for optimal capacity and safety. Circuit breakers are installed for each circuit.
- Testing: The electrician will conduct tests to ensure that everything is functioning correctly and safely.
- Inspection: Finally, the work will be inspected to confirm that it complies with local regulations and safety standards.
Maintaining Your Electrical Panel for Optimal Performance
Regular Inspections and Signs of Trouble
Routine maintenance is key to keeping your electrical panel in good condition. Homeowners should conduct regular inspections, looking for signs of trouble, such as discoloration, moisture, burnt odors, or unusual sounds. Scheduling professional inspections every few years can help identify potential issues before they become serious.
Best Practices for Panel Maintenance
To maintain your electrical panel effectively, follow these best practices:
- Keep the area around the panel clear of clutter to allow for easy access.
- Avoid overloading circuits by managing electrical usage throughout the home.
- Be proactive about any unusual behavior, such as flickering lights or panel noises. Address issues promptly with a qualified electrician.
When to Consult a Professional Electrician
It is advisable to consult a professional electrician if any signs of trouble are detected or if your electrical needs change, such as remodeling or installing new appliances. Regular consultations and inspections help ensure that your electrical panel operates efficiently, safely, and in compliance with current codes.